Cut, Colour, Clarity and Carats
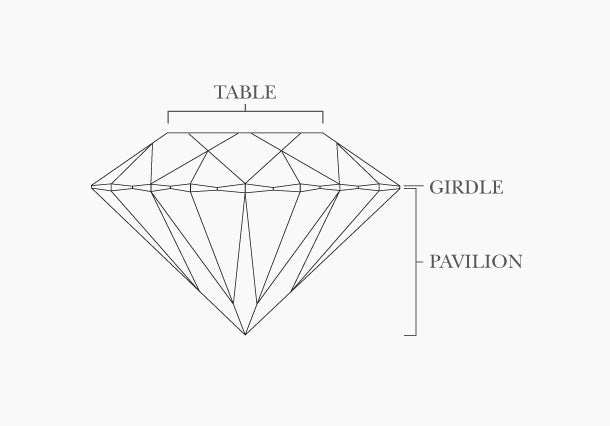
CUT
Gemologists agree that the cut of a diamond is the key to its brilliance. When comparing 2 diamonds with the same colour, a diamond that is cut with the right proportions will be much more brilliant than a poorly cut diamond. Therefore, if a diamond has a beautiful colour and good clarity, but is incorrectly cut , it will lose a lot in appearance. By cut, we mean the finish, the dimensions, the return of the light to the eye as well as the polishing and the symmetry. It goes without saying that these notions of cut represent an essential factor in the beauty and quality of a diamond, which only an experienced craftsman can master.
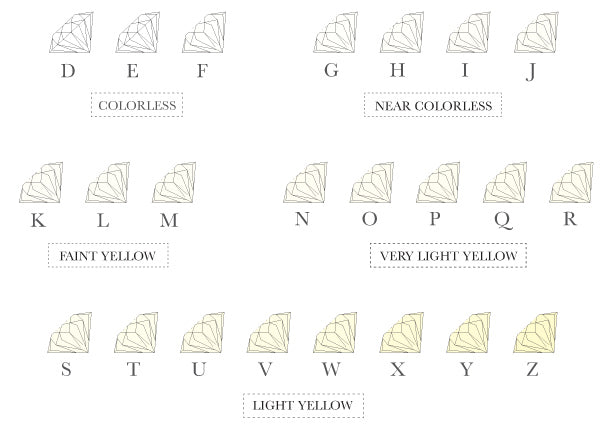
COLOUR
Diamonds are also classified by colour. Since the most sought-after colour is colourless, or the absence of colour, the less coloured the diamond , the higher its value. According to the diamond coloured classification scale published by the GIA (Gemological Institute of America), diamonds are classified from colourless to coloured (from white to yellow to brown) using the different letters of the alphabet. The colour-grading begins with the letter D, which represents the colourless and continues to the letter Z, according to the growing presence of colour. Thus, the perfect note for a diamond is not an A, but a D! Part of a separate class, "fancy" coloured diamonds can have very high value given their rarity and colour intensity.
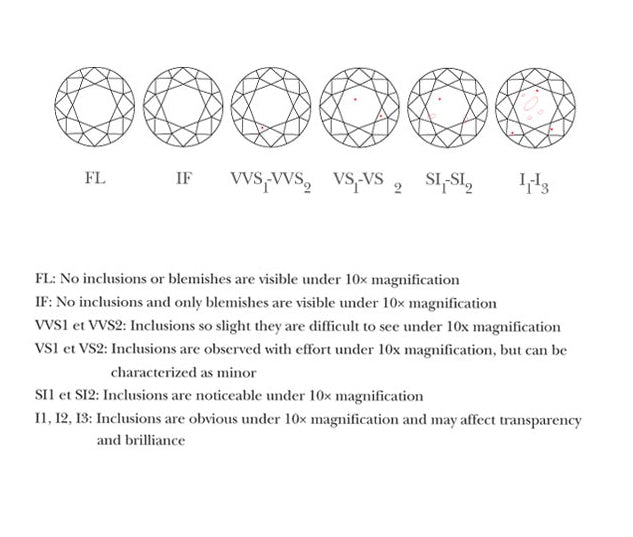
CLARITY
Because they form deeply in the earth, most diamonds contain internal foreign bodies, called inclusions, and external defects. In the vast majority of cases, the inclusions are caused by small black carbon crystals that can be trapped when forming diamonds. Diamonds with very few foreign bodies are rarer and, of course, will see their value increased. Using the International Diamond ™ classification system, created by GIA, we classify diamonds by category of clarity. In the determination of clarity, we must consider the position, quantity, size, color and nature of the impurities visible under 10x magnification.

CARAT
The weight of diamonds is one of the determining elements of its price. The measurement unit used to determine the weight of a diamond is the carat. A carat is divided into 100 points; Thus, a 25 points diamond is equivalent to a quarter of a carat, and a 50 points is equivalent to half a carat. Large stones being rare, the price of a diamond evolves exponentially depending on its weight.
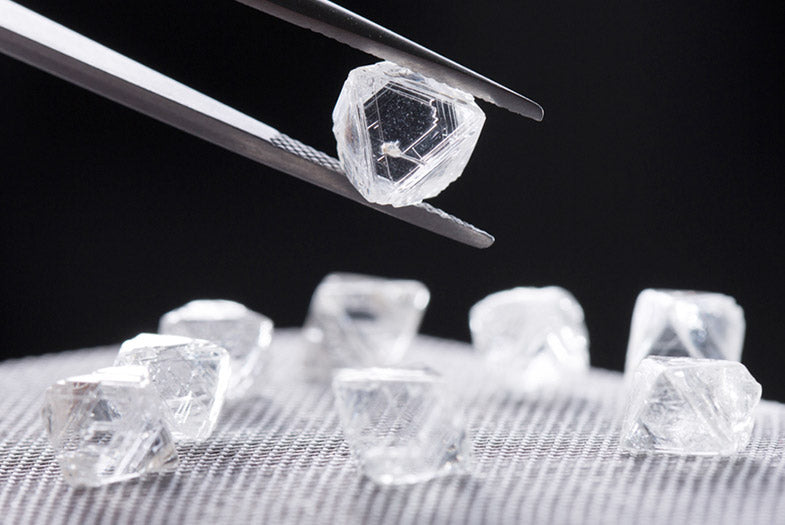

Natural Diamonds
Natural diamonds are diamonds that were created in nature millions of years ago. Created under intense heat and high pressure, natural diamonds are as unique as they are rare. This is precisely what gives them their value. Coming mainly from Canada, St-Onge natural diamonds are still the most prized today.
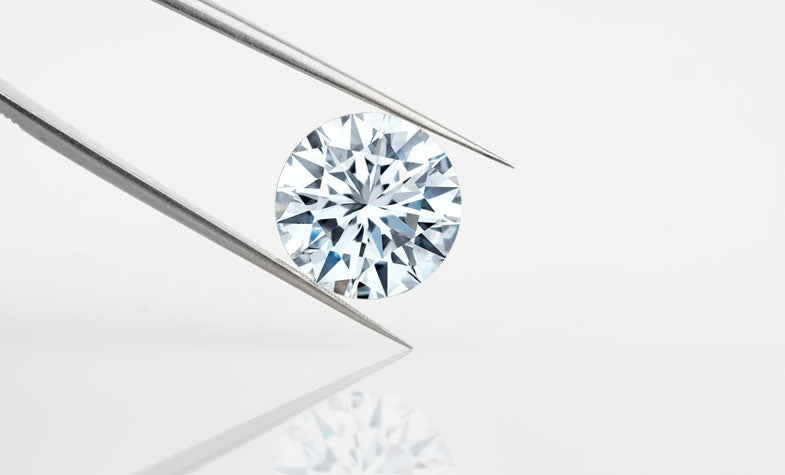

Lab Grown Diamonds
Lab grown diamonds (or synthetic diamonds) have the same chemical, physical and optical characteristics as natural diamonds. They are created in a laboratory using state-of-the-art technologies reproducing the same conditions under which natural diamonds formed, thus speeding up the manufacturing process. Lab grown diamonds is an alternative to natural diamonds.